Recommendations
Clearly articulate your purpose and define your sustainability strategy: Best-in-class companies identify a corporate purpose that encompasses sustainability goals and build a culture around it. A clear statement of purpose unites executives, directors and investors on the company’s priorities, and creates the link between strategy and capital allocation decisions. To create competitive advantage, more is required than convergence to industry standards – companies must differentiate strategically and develop approaches difficult to imitate.
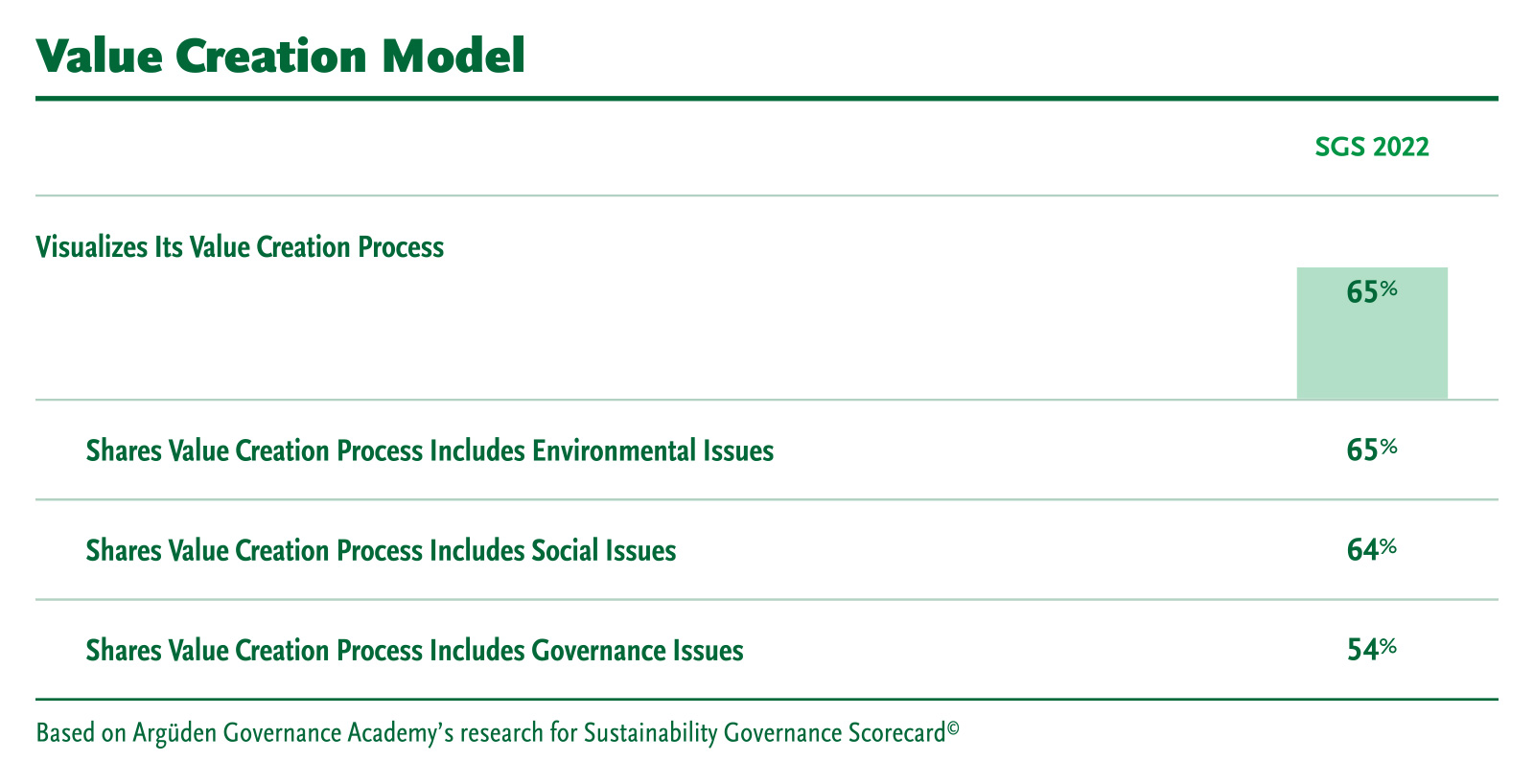
Visualize a holistic, sustainable value creation model: A value creation model forms the basis of a companies’ vision for long-term value creation. Companies should define tangible and intangible assets as a medium for value creation for both internal and external stakeholders. These capitals can be broadly defined as financial, manufactured, intellectual, human, social & relationship, and natural capital. This requires the company to evaluate the relationship between different functions towards achieving its strategic goals. Companies should also show how inputs link to outputs and outcomes.
Measure and disclose outcomes for external and internal stakeholders: Outcomes should be defined and quantified not just for shareholders but also for relevant external and internal stakeholders.
Adopt integrated thinking/reporting: Best examples of holistic thinking on value creation are found in companies that embrace Integrated Reporting. Integrated Reporting is a holistic tool to help companies tell the story of how they create value now and in the future. It is also a transparency and communication tool and can form the basis of constructive dialogue with investors as well as other stakeholders.
